
Garlic
Egyptian garlic is renowned for its robust, pungent flavor and versatile culinary uses. This aromatic bulb has a papery white skin and is divided into multiple cloves, each with a strong, spicy taste. Garlic is a staple in many cuisines and is used to enhance the flavor of a wide variety of dishes, from savory stews to roasted meats and vegetable dishes.
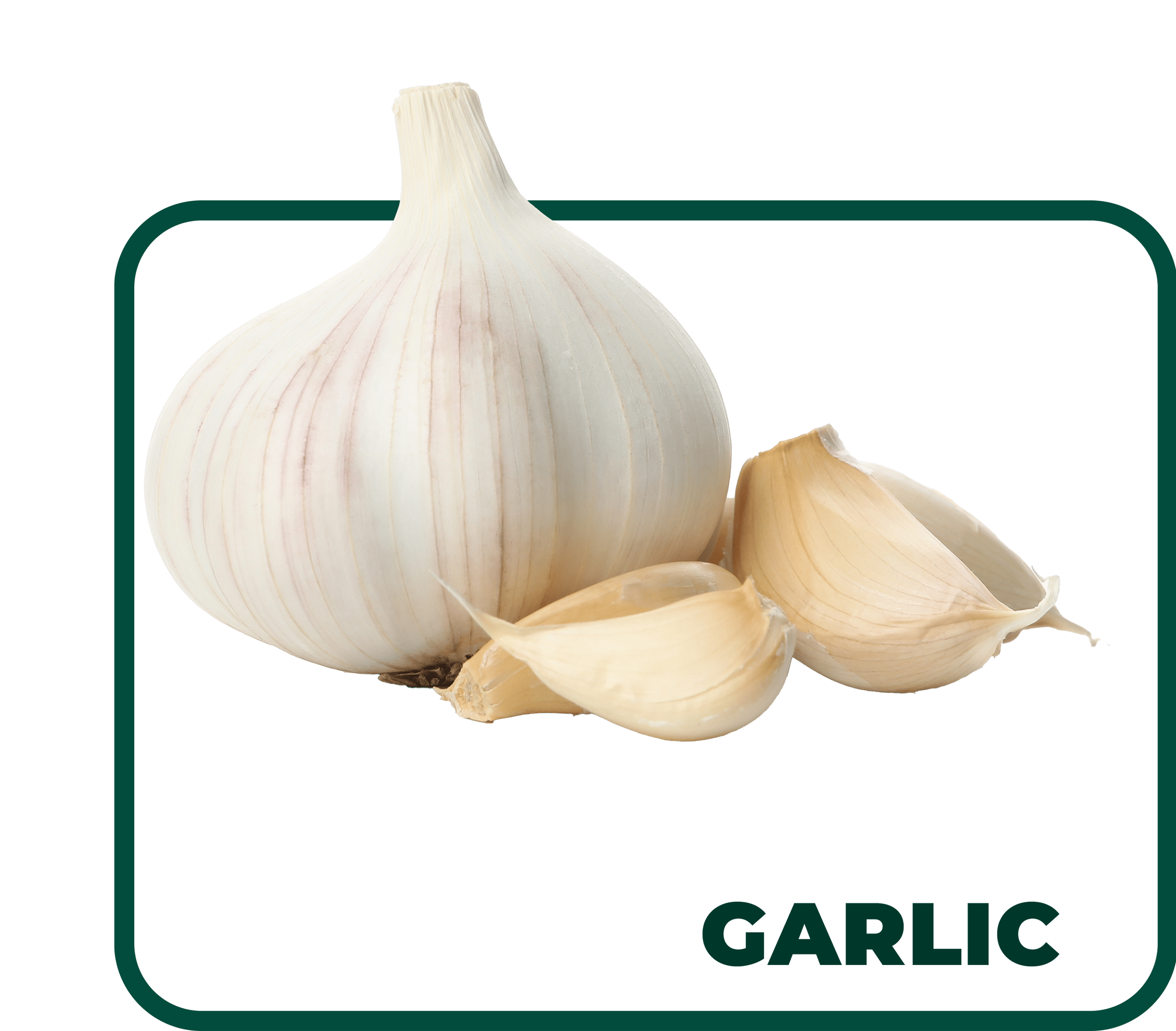
Garlic is typically planted in the fall, about 4 to 6 weeks before the first frost, allowing the cloves to establish roots before winter. It prefers well-drained soil with plenty of sunlight and requires a cool period to develop properly. Garlic is usually ready for harvest in mid to late summer, around 8 to 9 months after planting. Harvesting involves digging up the bulbs when the lower leaves begin to yellow and dry out, and then allowing them to cure in a dry, cool place before storing.
Consuming Egyptian garlic can support cardiovascular health, enhance immune function, and reduce inflammation. The antioxidants in garlic help protect cells from oxidative damage and support heart health by improving blood circulation and reducing cholesterol levels. Garlic’s anti-inflammatory properties can help alleviate symptoms of inflammation and support overall immune health. Additionally, garlic may have antimicrobial properties, which can help fight infections and support digestive health.
Garlic is rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins C and B6, manganese, and selenium. It contains compounds like allicin, which has demonstrated strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Garlic is known for its potential health benefits, including supporting heart health, boosting the immune system, and promoting overall well-being. The sulfur compounds in garlic, like diallyl disulfide, contribute to its unique flavor and health benefits.
